In the ever-evolving landscape of search engine optimization (SEO), practitioners constantly seek effective strategies to improve website rankings. Among these techniques, Private Blog Networks (PBNs) remain one of the most controversial and misunderstood approaches. Despite significant changes in search engine algorithms and a push toward more ethical SEO practices, PBNs continue to exist in the shadows of the industry, prompting important questions about their legitimacy, effectiveness, and associated risks.
This comprehensive guide explores what Private Blog Networks are, how they function within the SEO ecosystem, why some SEO practitioners still use them despite the risks, and the potential consequences of implementing PBN strategies in your SEO campaigns. Whether you’re a website owner curious about various link-building approaches or an SEO professional evaluating different strategies, understanding PBNs is crucial for making informed decisions about your digital marketing efforts.
What Is a Private Blog Network (PBN)?
Definition and Core Concept
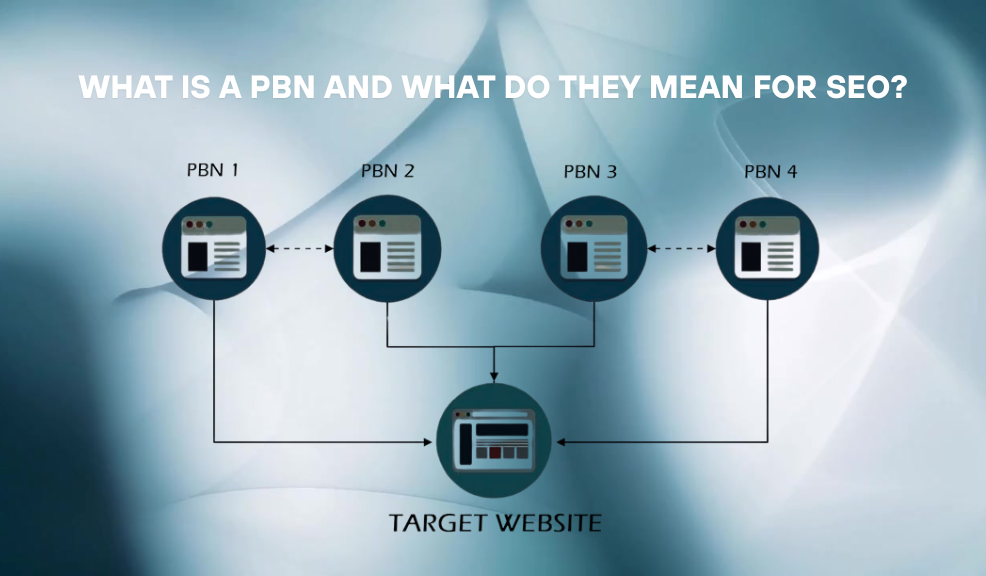
A Private Blog Network (PBN) is a network of websites or blogs created specifically to build backlinks to a main “money site” with the purpose of manipulating search engine rankings. These websites are typically controlled by the same individual or organization but are designed to appear as if they’re owned and operated by different entities.
The fundamental premise behind a PBN is to create what appears to be a network of independent, authoritative websites that link to your main website, thereby passing link equity (also known as “link juice”) to improve search engine rankings. The “private” aspect refers to the fact that these websites are privately owned and controlled by the same person or organization, though this ownership connection is deliberately obscured from public view.
Key Components of a PBN
A typical Private Blog Network consists of several essential elements:
- Expired or Auctioned Domains: PBN builders often purchase expired domains with existing authority, established backlink profiles, and history. These domains may have once hosted legitimate websites that accumulated authority over time before being abandoned.
- Separate Hosting Accounts: To avoid footprints that might reveal the connection between sites, PBN operators typically use different hosting providers or IP addresses for each website in the network.
- Unique WHOIS Information: To further mask the common ownership, different WHOIS records (domain registration information) are used, often through privacy protection services or by registering domains under different entities.
- Content Creation: PBN sites are populated with content related to the niche of the main website. This content may vary in quality but is generally created to make the sites appear legitimate to both users and search engines.
- Link Placement: Strategic backlinks pointing to the main website are placed within the content of PBN sites, often with optimized anchor text to target specific keywords.
- Separate Analytics and Tracking: Different analytics accounts and tracking implementations help prevent leaving digital footprints that could connect the network sites.
How PBNs Operate in SEO
PBNs operate on a fundamental principle of search engine optimization: backlinks from authoritative websites serve as “votes of confidence” that improve a site’s rankings. The strategic process typically follows these steps:
- Domain Acquisition: The process begins with identifying and purchasing expired or auction domains with existing authority, often measured by metrics like Domain Rating (DR), Domain Authority (DA), or referring domains.
- Website Restoration: After acquisition, operators may restore the domain to a state similar to its original content using archives, or create new content that aligns with the domain’s history and the target website’s niche.
- Establishing Uniqueness: Each PBN site is set up with different hosting, themes, content styles, and technical implementations to appear as independent websites.
- Content Development: Content is created or acquired for each PBN site, often focusing on topics related to the main website’s industry or niche.
- Link Building Strategy: Backlinks to the main website are strategically placed within the content, with careful attention to anchor text distribution, link velocity, and contextual relevance.
- Network Management: The network requires ongoing maintenance, including domain renewals, content updates, and monitoring for signs that search engines have identified the network.
The ultimate goal is to create a seemingly natural ecosystem of independent websites that endorse the main website, thereby improving its search engine rankings for targeted keywords.
The History and Evolution of PBNs
Origin and Early Use
Private Blog Networks have roots in the earlier days of SEO when search engine algorithms heavily weighted backlinks in ranking determinations without sophisticated means to evaluate link quality or detect manipulation. Early versions of PBNs emerged in the late 2000s as SEO practitioners recognized the powerful impact that multiple backlinks could have on rankings.
In these early iterations, PBNs were often less sophisticated, sometimes consisting simply of multiple blogs created on free platforms or inexpensive domains. As search engines began to develop more nuanced algorithms, these rudimentary networks quickly lost effectiveness.
Evolution in Response to Algorithm Updates
Google’s algorithm updates have played a significant role in shaping PBN practices:
- Penguin Update (2012): This major algorithm update specifically targeted link schemes and manipulative link-building practices. After Penguin, PBNs became more sophisticated, with greater emphasis on quality content and natural link profiles.
- Manual Action Penalties (2013-2014): Google began taking more aggressive manual actions against PBNs, including a significant wave of penalties in 2014 that affected many prominent networks.
- Further Refinements (2015-Present): Subsequent updates to Google’s algorithms have incorporated more advanced machine learning capabilities to identify unnatural link patterns, forcing PBN operators to develop increasingly sophisticated methods to avoid detection.
As search engines became better at identifying and penalizing manipulative link-building tactics, PBNs evolved from simple blog networks into more complex ecosystems of seemingly unrelated websites with careful attention to removing any detectable patterns or footprints.
Current State of PBNs
Today’s PBNs bear little resemblance to their early counterparts. Modern private blog networks often feature:
- High-quality domains with clean link histories and established authority
- Professional-looking website designs and branding
- Regular content updates that mimic legitimate publishing schedules
- Diverse hosting arrangements across multiple providers and server locations
- Sophisticated approaches to masking ownership connections
- Strategic link placement that mimics natural editorial decisions
- Mixed linking patterns that include outbound links to authority sites
Despite these advancements, search engines continue to refine their ability to detect PBNs, leading to an ongoing cat-and-mouse game between PBN operators and search engine algorithms.
Why Some SEO Practitioners Still Use PBNs
Perceived Benefits of PBNs
Despite the risks, some SEO practitioners continue to employ PBN strategies for several reasons:
1. Control Over Backlink Acquisition
PBNs offer complete control over the link-building process, including:
- Exact anchor text selection
- Precise placement of links within content
- Timing of link publication
- Contextual relevance surrounding the link
This level of control is difficult to achieve with legitimate link-building strategies that depend on convincing independent website owners to provide backlinks.
2. Cost Efficiency for Multiple Projects
For agencies or individuals managing multiple websites, a well-established PBN can serve as an internal link-building resource that reduces the ongoing cost of acquiring backlinks through other means. After the initial investment in setting up the network, the marginal cost of creating additional links is relatively low.
3. Competitive Advantage in Difficult Niches
In highly competitive industries where all legitimate link-building avenues have been exhausted, PBNs may provide a way to gain an edge over competitors following more traditional SEO practices. This is particularly true in industries where natural link acquisition is challenging.
4. Speed of Impact
While legitimate link-building strategies often require months or years to show significant results, PBNs can potentially deliver ranking improvements in a matter of weeks, appealing to those seeking faster returns on their SEO investments.
Motivations Behind PBN Use
Understanding the underlying motivations helps explain why some choose to accept the risks associated with PBNs:
- Short-term Business Models: Websites focused on quick monetization rather than building long-term brand value may prioritize immediate rankings over sustainable practices.
- Client Pressure: SEO agencies sometimes face unrealistic timeline expectations from clients, pushing them toward higher-risk strategies that deliver faster results.
- Competitive Analysis: Observing competitors successfully using PBNs (at least temporarily) may influence others to adopt similar tactics.
- Risk Tolerance: Some SEO practitioners approach their work with a higher risk tolerance, viewing potential penalties as an acceptable business risk compared to the potential rewards.
The Risks and Consequences of Using PBNs
Search Engine Penalties
The most significant risk associated with PBNs is search engine penalties, which can manifest in different forms:
1. Algorithmic Penalties
Search engines use algorithmic signals to identify manipulative link patterns. Sites benefiting from PBN links may experience automatic ranking decreases when these algorithms detect unnatural link profiles. These penalties may affect specific keywords or the entire website, depending on the extent of the manipulation.
2. Manual Actions
More severe than algorithmic penalties, manual actions occur when a search engine reviewer manually identifies a website as violating quality guidelines. Google may issue manual actions specifically for “unnatural links to your site” when they detect participation in link schemes like PBNs. These penalties appear in Google Search Console and can dramatically impact a site’s visibility.
3. Deindexing
In extreme cases, search engines may completely remove PBN sites from their index, eliminating any value they might pass to the main website. Additionally, websites that repeatedly violate guidelines through manipulative tactics risk being deindexed themselves.
Financial Consequences
Beyond direct penalties, PBNs carry significant financial risks:
- Investment Loss: The considerable investment in domain acquisition, hosting, content creation, and maintenance becomes worthless if the network is discovered and penalized.
- Recovery Costs: Recovering from penalties often requires hiring experts to perform link audits, disavow manipulative links, and create new content—expenses that frequently exceed the original PBN investment.
- Revenue Impact: Traffic and ranking losses following penalties directly impact revenue, sometimes catastrophically for businesses heavily dependent on organic search traffic.
- Opportunity Cost: Resources invested in building and maintaining PBNs could have been directed toward sustainable SEO strategies with long-term benefits.
Reputational Damage
Using PBNs can also result in lasting reputational consequences:
- Brand Perception: If customers or industry peers discover a business has engaged in manipulative SEO tactics, it may damage trust and credibility.
- Client Relationships: For agencies, penalties resulting from PBN use can destroy client relationships and lead to contract terminations, refund demands, or even legal action.
- Industry Reputation: SEO professionals known for using black hat techniques may find it difficult to secure employment or clients seeking legitimate, sustainable strategies.
How Search Engines Detect PBNs
Search engines have developed sophisticated methods to identify Private Blog Networks:
Technical Footprints
Despite efforts to hide connections, PBNs often leave detectable technical patterns:
- Hosting Relationships: Even with different hosting providers, IP addresses, name servers, and DNS records can reveal connections between supposedly independent websites.
- Shared Resources: Common themes, plugins, analytics codes, or advertising accounts across multiple sites may flag potential PBN activity.
- Registration Patterns: Similar registration dates, renewal patterns, or registrar usage can indicate common ownership.
- Code Similarities: Identical HTML structure, CSS formatting, or JavaScript implementations may reveal sites developed by the same person.
Content and Link Analysis
Beyond technical signals, content and linking patterns provide additional detection clues:
- Content Fingerprinting: AI-powered tools can identify content with similar writing styles, formatting approaches, or publishing patterns across multiple domains.
- Link Graph Analysis: Advanced algorithms analyze the entire link ecosystem to identify unnatural clusters of sites linking to the same targets with similar patterns.
- Temporal Link Analysis: Suspicious timing of link acquisitions, especially when multiple links appear across different websites within a short timeframe, may trigger closer scrutiny.
- Contextual Analysis: Links that appear forced, irrelevant to the surrounding content, or overly optimized with commercial anchor text raise red flags.
Machine Learning and AI
Modern search engines employ machine learning to detect increasingly subtle patterns:
- Pattern Recognition: AI systems analyze thousands of confirmed PBN cases to identify common characteristics not obvious to human reviewers.
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models flag statistical anomalies in linking patterns, content publication, or technical implementations that deviate from normal website behavior.
- Network Analysis: Advanced algorithms map relationships between seemingly unrelated websites to uncover hidden connections indicative of coordinated link schemes.
As these detection capabilities continue to advance, the long-term viability of PBNs becomes increasingly questionable.
Ethical Alternatives to PBNs
For those seeking sustainable, risk-free alternatives to PBNs, several legitimate link-building strategies offer long-term value:
Content-Driven Link Acquisition
Creating genuinely valuable content naturally attracts backlinks:
- Original Research: Publishing industry studies, surveys, or data analysis provides unique value that others naturally reference and link to.
- Comprehensive Guides: In-depth, authoritative content that thoroughly covers important topics often earns links as a reference resource.
- Visual Assets: Infographics, diagrams, and other visual content are highly shareable and frequently attract backlinks when distributed properly.
- Expert Interviews: Featuring industry experts in your content can lead to natural links when those experts share the content with their audiences.
Relationship-Based Link Building
Building authentic industry relationships creates sustainable link opportunities:
- Guest Posting: Contributing valuable content to reputable websites in your industry can include contextual links when relevant to the topic.
- HARO and Media Outreach: Serving as an expert source for journalists and bloggers through platforms like Help a Reporter Out (HARO) generates high-quality media mentions and links.
- Podcast Appearances: Being interviewed on industry podcasts typically results in links from episode pages and show notes.
- Community Participation: Active involvement in industry forums, communities, and social platforms builds relationships that can lead to natural link opportunities.
Digital PR and Brand Building
Broader marketing efforts that generate backlinks as a secondary benefit:
- Newsworthy Content: Creating genuinely newsworthy content that journalists want to cover can generate high-authority links from media outlets.
- Resource Creation: Developing tools, calculators, or resources valuable to your industry often attracts links from those who find them useful.
- Scholarships and Community Initiatives: Supporting educational or community programs can earn links from educational institutions and community organizations.
- Events and Sponsorships: Hosting or sponsoring industry events frequently results in links from event websites, partners, and attendees.
These ethical approaches may require more time and effort than PBNs but provide sustainable results without the associated risks.
Should You Use a PBN for Your SEO Strategy?
Evaluating the Risk-Reward Ratio
When considering whether to implement a PBN strategy, evaluate:
- Business Model: Is your website a long-term brand investment or a short-term monetization project? Long-term businesses have more to lose from penalties.
- Risk Tolerance: What would the impact of a significant traffic loss be on your business? Some businesses can weather temporary setbacks, while others would face existential threats.
- Resource Availability: Do you have the technical expertise and resources to create a truly undetectable PBN? Amateur implementations are easily discovered.
- Competitive Landscape: Are your competitors using PBNs successfully? While this doesn’t justify the tactic, it provides context for your decision.
- Ethical Considerations: Beyond practical concerns, consider whether manipulative tactics align with your personal and business values.
Questions to Ask Before Proceeding
Before implementing any link-building strategy, ask yourself:
- Would I be comfortable explaining this tactic to my customers?
- If Google representatives reviewed my SEO strategy, would I be concerned?
- Am I building lasting value or seeking a temporary advantage?
- Is the potential short-term gain worth the long-term risk?
- Have I exhausted all legitimate link-building opportunities?
Industry Expert Consensus
The overwhelming consensus among respected SEO industry leaders is that PBNs represent an unsustainable and increasingly risky approach:
- Most recognized SEO experts publicly advise against PBN use due to the significant risks
- Search engine representatives consistently warn against link schemes including PBNs
- Case studies of penalties demonstrate the potential consequences
- The trend in SEO is unmistakably toward sustainable, value-based strategies
Private Blog Networks represent a high-risk approach to link building that continues to exist despite increasing sophistication in search engine algorithms. While they may offer short-term ranking benefits, the potential consequences—ranging from search penalties to brand damage—make them increasingly difficult to justify for businesses focused on sustainable growth.
The evolution of search algorithms continues to prioritize genuinely valuable content and authentic endorsements, making ethical SEO practices not only safer but often more effective in the long run. Rather than investing in elaborate schemes to manipulate rankings, businesses typically achieve better results by directing those resources toward creating exceptional content and user experiences worthy of natural recommendation.
For most website owners and SEO professionals, the question isn’t whether PBNs can work in the short term—it’s whether the temporary advantage is worth the substantial risks and opportunity costs. In a digital marketing landscape increasingly focused on authenticity and value, sustainable strategies aligned with search engine guidelines nearly always represent the wiser investment.